
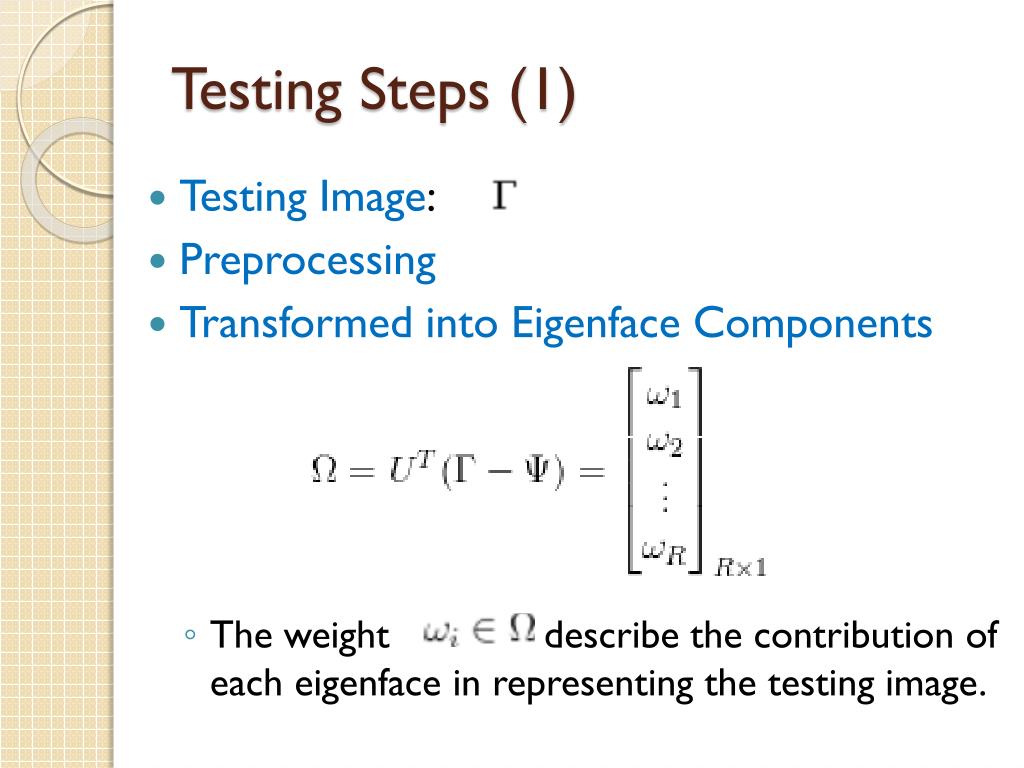
PCA METHOD FOR HYPERIMAGE SERIES
To check the quality of the fused image few quality matrices are like Peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR), Mean square error (MSE), Average gradient (AG), Mutual information (MI) etc.Principal components and related quantities cols ndarrayĪrray of indices indicating columns used in the PCA rows ndarrayĪrray of indices indicating rows used in the PCAīox plots of the individual series R-square against the number of PCs. Therefore, few of the image fusion techniques for image fusion like Averaging image fusion method, Maximum image fusion method, Minimum image fusion method, Discrete Wavelet transform based fusion, Principal component analysis (PCA) based fusion, Low pass filter (HPF), Intensity hue saturation (IHS) etc. MS image is the composite of Red (R), Green (G), Blue (B) bands and PAN image is the gray scale image. The fused image is inter compare with the other method on the basis of quality matrices and from the fused image detected water area of small as well as large water body. Remote sensing of water body detection is fundamentally rooted of electromagnetic radiation from the object. The resultant image of the input image will be more informative and consummated rather than any of the input images, which makes it easy to categorize, compare, and evaluate the existing quality matrices of image fusion methods. Remote sensing is the collection of the information from the image capture by the sensor.
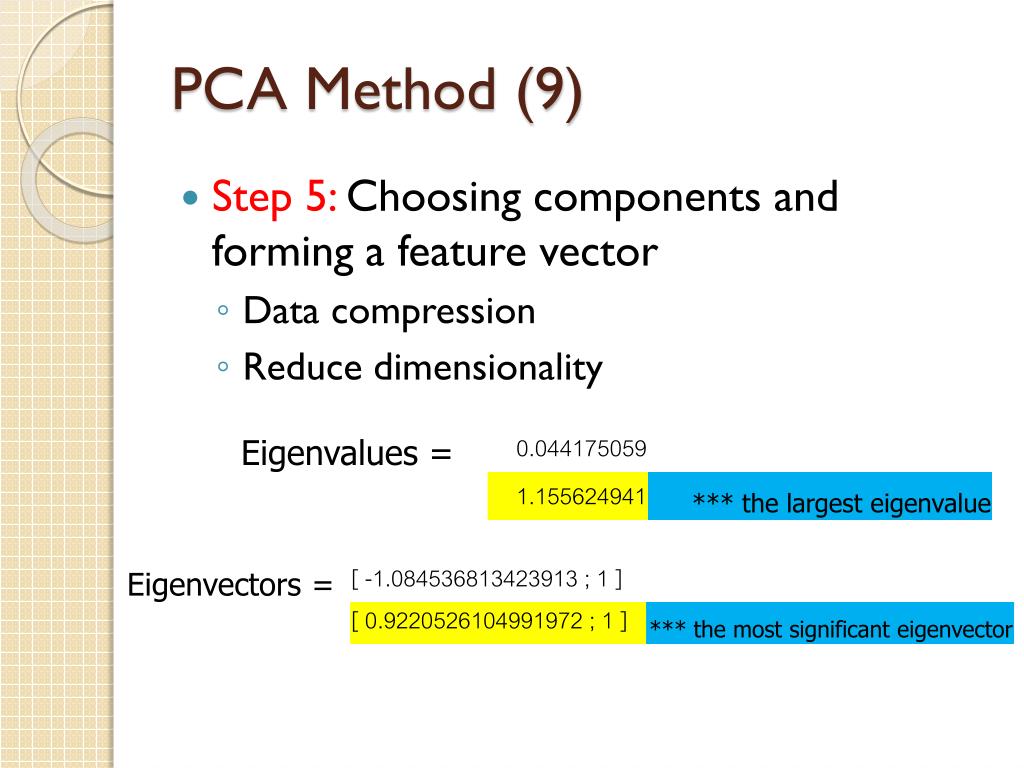
PCA METHOD FOR HYPERIMAGE HOW TO
In addition, targets of interest like persons or cars How to cite this article Toet (2016), Iterative guided image fusion. As a result, additive noise may obscure or distort relevant image details. Additive noise can be modelled as a random signal that is simply added to the original signal. While different types of noise may result from several processes associated with the underlying sensor physics, additive noise is typically the predominant noise component encountered in II and NIR imagery (Petrovic & Xydeas, 2003). For instance, in nighttime (low-light) outdoor surveillance applications, intensified visual (II) or near-infrared (NIR) imagery often provides a detailed but noisy representation of a scene. Effective combinations of complementary and partially redundant multispectral imagery can therefore visualize information that is not directly evident from the individual input images. The information provided by different sensors registering the same scene can either be (partially) redundant or complementary and may be corrupted with noise. INTRODUCTION The increasing deployment and availability of co-registered multimodal imagery from different types of sensors has spurred the development of image fusion techniques. The method has a simple implementation and is computationally efficient. Application to multiband visual (intensified) and thermal infrared imagery demonstrates that the proposed method obtains state-of-the-art performance for the fusion of multispectral nightvision images. The final fused image is obtained as the weighted recombination of the individual residual layers and the mean of the approximation layers at the coarsest spatial scale. Guided filtering of the binary weighting maps with their corresponding source images as guidance images serves to reduce noise and to restore spatial consistency.

Next, at each spatial scale binary weighting maps are obtained as the pixelwise maximum of corresponding source saliency maps. Then, frequency-tuned filtering is used to compute saliency maps at successive spatial scales. First, size-selective iterative guided filtering is applied to decompose the source images into approximation and residual layers at multiple spatial scales.
The proposed multi-scale image fusion scheme achieves spatial consistency by using guided filtering both at the decomposition and at the recombination stage of the multi-scale fusion process. When applied in an iterative mode, guided filtering selectively eliminates small scale details while restoring larger scale edges. Guided filtering can effectively reduce noise while preserving detail boundaries. We propose a multi-scale image fusion scheme based on guided filtering.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
